What Is The Cuticle? Unveiling Its Diverse Roles In Your Body And Beyond
When you hear the word "cuticle," what's the first thing that comes to mind? For many, it's that tiny strip of skin at the base of their fingernails, often pushed back or trimmed during a manicure. But what if we told you that the term "cuticle" encompasses far more than just your nails? It's a fascinating biological structure found in various forms across the human body, in animals, and even in plants, each serving a vital protective purpose. This article will delve into the multifaceted world of the cuticle, exploring its different manifestations, compositions, and crucial functions, helping you understand why this seemingly small detail plays such a significant role in health and survival.
More Than Just Your Nails: The Broad Definition of "Cuticle"
The term "cuticle" is a biological concept that refers to a protective outer layer, but its specific meaning can vary greatly depending on the context. In human anatomy, it's not just limited to the eponychium of the nail; it refers to various structures, including layers of epidermal cells or keratinocytes that produce keratin—a protein also found in animal horns. Essentially, a cuticle is a thin film or membrane that covers distinct structures of the body, whether human, animal, or plant, acting as a crucial barrier.
This widespread presence highlights its fundamental importance across different life forms. From the tips of your fingers to the surface of a leaf, the cuticle serves as a frontline defense, safeguarding delicate underlying tissues from external threats. Understanding this broader definition is key to appreciating its biological significance.
- Bladensburg High School Photos
- Alexis Doyle
- 66 Greenpoint Ave
- 1500 Calorie Meal Plan Indian Non Veg
- Karen Morse
The Cuticle on Your Nails: A Tiny Guardian
Let's start with the most commonly recognized cuticle: the one on your nails. While often seen as a minor aesthetic detail, this small layer of skin is a powerful protector.
What Exactly is the Nail Cuticle?
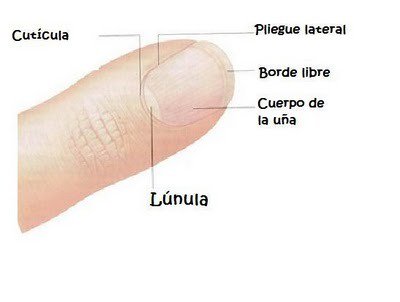
The nail cuticle is a thin layer of skin located along the bottom edge of your finger or toe, right where the nail meets the skin of the finger. This area is also known as the nail bed. Specifically, the nail cuticle is often described as dead cell tissue that sits right at the edge of the nail, forming part of the skin where the nail grows. It's a clear layer of skin situated on the nail bed.
It's important to distinguish the cuticle from the eponychium. While often used interchangeably, the cuticle is the dead skin over the nail bed, whereas the eponychium (or proximal seal) is the live tissue surrounding the nail. The cuticle is the intermediate layer of the proximal nail fold and the nail plate, forming a crucial seal at the base of the nail.
Why Do We Have Nail Cuticles? Its Crucial Functions
Despite its small size, the nail cuticle performs several indispensable functions:
- Protection Against Infections: The primary purpose of the nail cuticle is to protect your nails from fungi, bacteria, and yeast. It acts as a protective barrier, preventing these harmful microorganisms from entering the delicate nail matrix, which is the part where nail growth originates. This thin layer of skin seals your skin to your nail, effectively blocking potential pathogens.
- Safeguarding the Nail Matrix: By sealing the nail matrix, the cuticle ensures that the new nail cells are produced in a clean and protected environment, contributing to healthy nail growth.
- Preventing Damage: It helps to shield the nail from external damage, maintaining its integrity and strength.
- Maintaining Moisture: The cuticle also helps to maintain the natural moisture balance of the nail and surrounding skin, preventing dryness and brittleness.
Cuticle Care: To Trim or Not to Trim?
In many beauty salons, it's common practice to remove the cuticle during a manicure to make nail polish application smoother and prevent it from lifting. However, this practice can be detrimental to nail health. Removing the cuticle compromises its protective barrier, making your nails more susceptible to infections and damage. Expert advice often suggests against cutting the cuticle. Instead, focus on:
- Hydration: Regularly moisturizing your cuticles with oils or creams can keep them soft, pliable, and healthy.
- Gentle Pushing: If desired, you can gently push back the cuticles using a specialized tool after softening them, rather than cutting them.
- Regeneration: Allow damaged cuticles to regenerate naturally, providing them with the necessary care to heal.
The Cuticle of Your Hair: The Armor of Your Strands
Beyond your nails, the term "cuticle" also refers to a critical component of your hair strands. This often-overlooked layer plays a monumental role in the appearance, strength, and overall health of your hair.
Understanding the Hair Cuticle
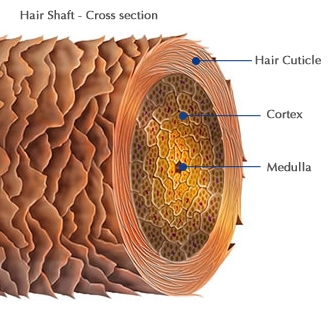
The hair cuticle is the outermost layer of the hair fiber. It's a transparent and hard layer formed from the keratinization of dead cells. This process generates tiny, overlapping scales, much like shingles on a roof or armor plates. These scales are flat and transparent, creating a protective shield for the inner parts of the hair shaft.
The hair cuticle is not simply one layer; it's composed of several layers of these keratinized scales. It's the first line of defense for the hair fiber, comparable to a protective armor for your hair strands.
The Vital Role of Hair Cuticles
The hair cuticle fulfills two primary functions: protection and maintenance:
- Protection: Its scaly structure acts as a formidable barrier, protecting the inner cortex and medulla of the hair from environmental damage, chemical treatments, and mechanical stress (like brushing and styling).
- Appearance and Feel: A healthy, smooth cuticle layer reflects light evenly, giving hair its characteristic shine and luster. When the scales lie flat, the hair feels soft and smooth. Conversely, a damaged or raised cuticle can lead to dull, frizzy, and rough-feeling hair.
- Moisture Retention: The cuticle also helps to seal in moisture, preventing the hair from drying out and becoming brittle.
Understanding the hair cuticle is crucial for proper hair care. Products and treatments often aim to smooth or strengthen this outer layer to improve hair health and appearance.
The Cuticle in the Plant World: A Waxy Shield
The concept of a protective outer layer extends even further into the realm of botany. Plants, too, possess a cuticle, which is essential for their survival in diverse environments.
Plant Cuticle Basics
In the botanical field, the cuticle is a membrane composed of a cellular layer. More specifically, it's a waxy film that covers the surface of plants, particularly their leaves, stems, and fruits. This waxy layer is secreted by the epidermal cells of the plant.
How Plant Cuticles Protect
Despite being exposed to various environmental conditions, the plant cuticle provides crucial protection:
- Protection Against Mechanical Damage: It offers a physical barrier against scrapes, tears, and other forms of physical injury.
- Water Loss Prevention: One of its most critical functions is to prevent excessive water loss through transpiration, especially in hot or dry climates. The waxy nature of the cuticle makes it impermeable to water, helping the plant retain essential moisture.
- UV Radiation Barrier: The cuticle can also absorb or reflect harmful ultraviolet (UV) radiation, protecting the underlying photosynthetic cells from damage.
- Pathogen Defense: It acts as a barrier against pathogens such as bacteria, fungi, and viruses, preventing them from penetrating the plant's tissues and causing disease.
The thickness and composition of the plant cuticle can vary depending on the plant species and its habitat, reflecting adaptations to different environmental challenges.
Conclusion
As we've explored, the term "cuticle" is a fascinating example of how a single biological concept can manifest in diverse forms, each serving a vital protective role across different biological contexts. Whether it's the thin layer of skin guarding your nail matrix, the scaly armor protecting your hair strands, or the waxy film shielding a plant from the elements, the cuticle consistently acts as a crucial barrier. Its primary function is always protection: safeguarding delicate structures from infections, damage, and environmental stressors. Understanding "what is the cuticle" means appreciating this remarkable, multifaceted guardian that plays an indispensable role in maintaining health and integrity across the living world.
Cutícula - EcuRed

qué son las cutículas y cómo cuidarlas para que no se resequen
Entender la cutícula del cabello y tu cabello natural: 3 cosas que